Texan’s Perspectives on and Experiences with
Diabetes Prevention
EHF’s annual polls help to guide the foundation’s work. We believe in the importance of incorporating the voices of Texans on health and health policy issues with the hope of integrating their opinions in decision-making conversations at state and local levels. This year, we asked Texans to weigh in on three key issues in public health: maternal mortality, diabetes prevention, and food & nutrition security.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 Diabetes is a long-term condition that results in too much sugar circulating in the blood. Type 2 Diabetes can lead to disorders of the circulatory, nervous, and immune systems.
An individual who is considered prediabetic has a higher than normal blood sugar level and is at high risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes. Individuals can prevent prediabetes from progressing to Type 2 Diabetes by incorporating diet and exercise changes into their lifestyle. Learn more about Type 2 Diabetes here.
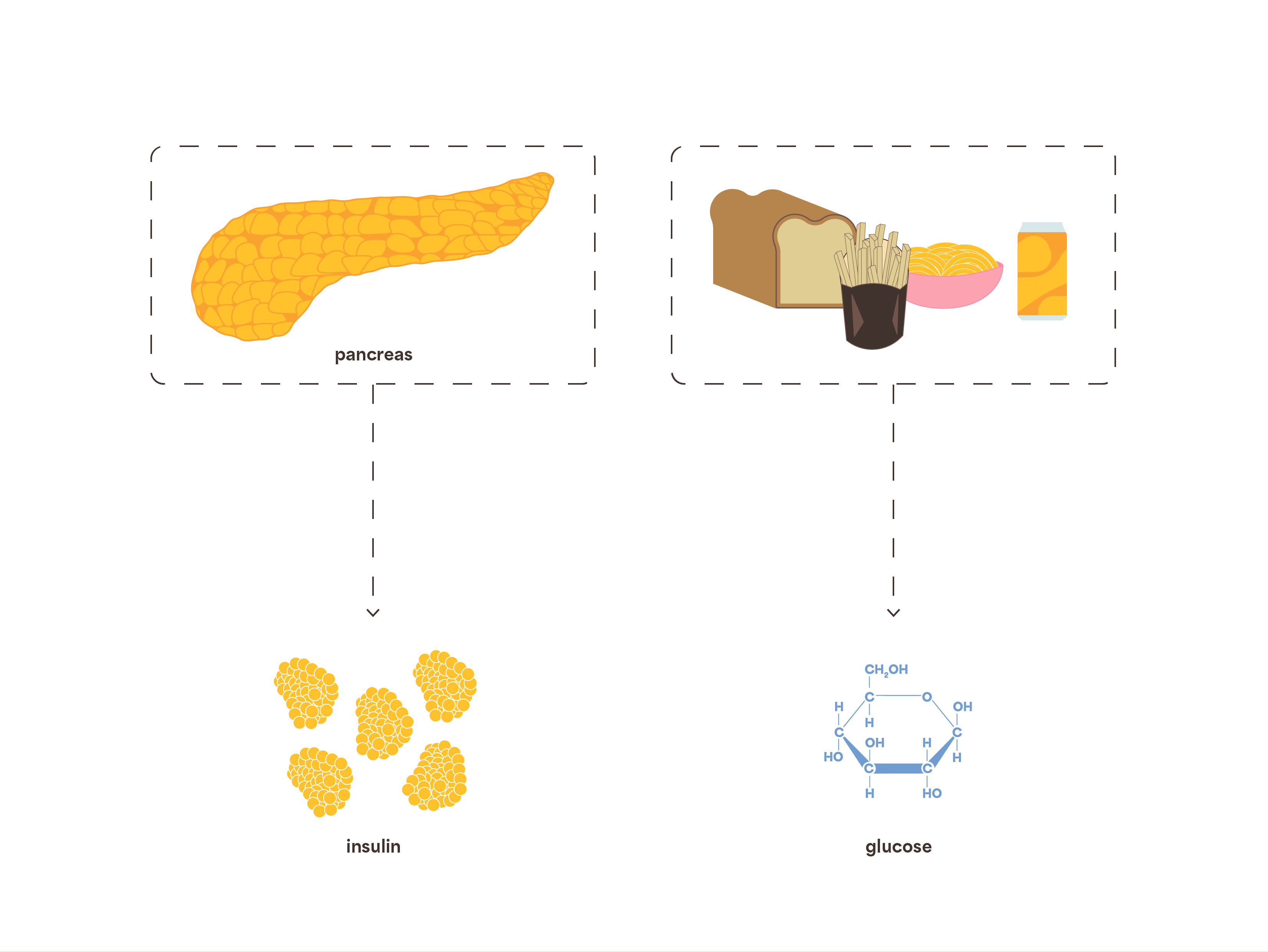
The pancreas releases a hormone called insulin, a chemical messenger that is essential for the entry of the glucose into cells.

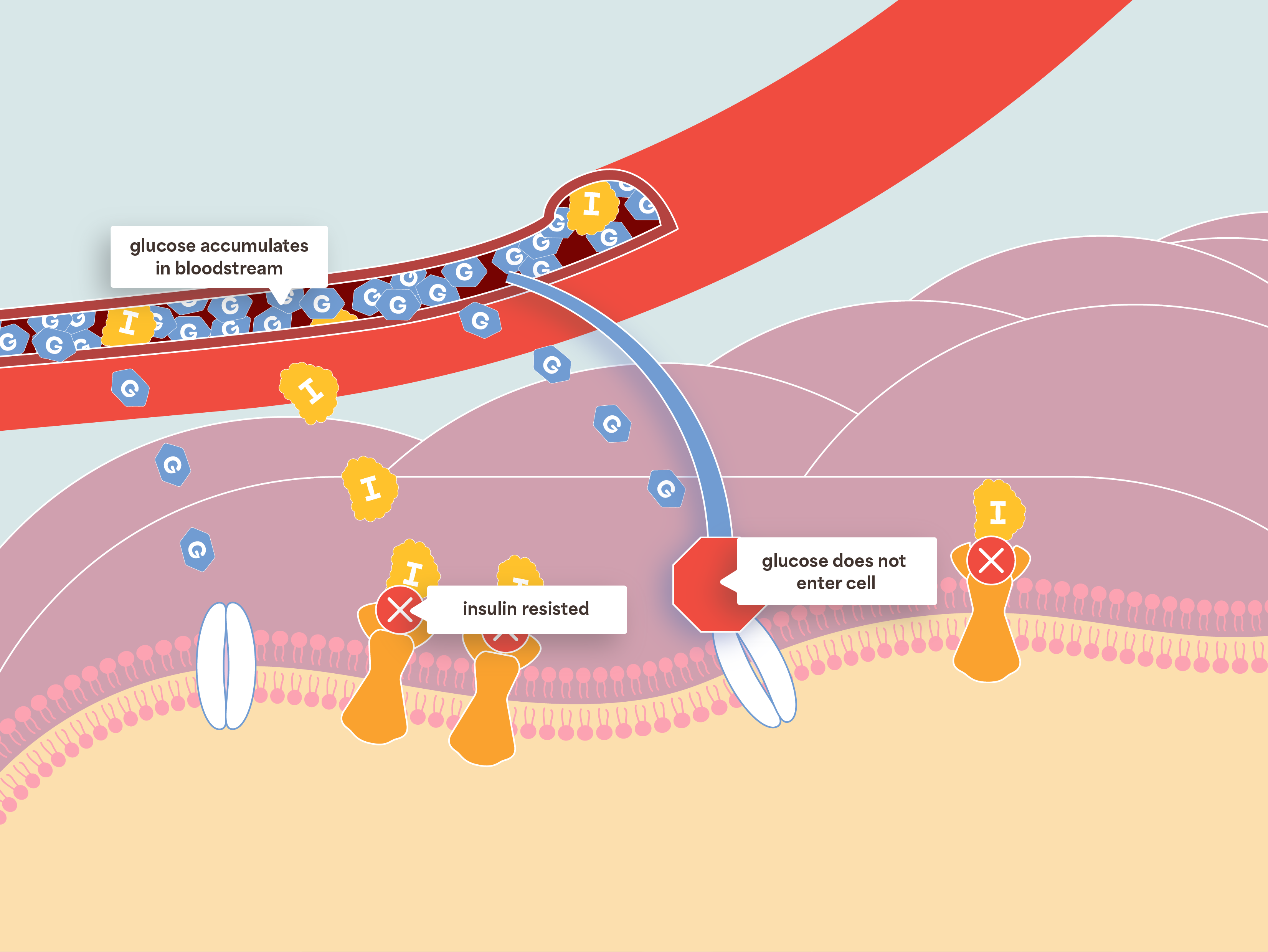
Risk factors for insulin resistance include: high blood sugar, high triglycerides, high LDL (bad) cholesterol, low HDL (good) cholesterol, family history of diabetes, and physical inactivity.
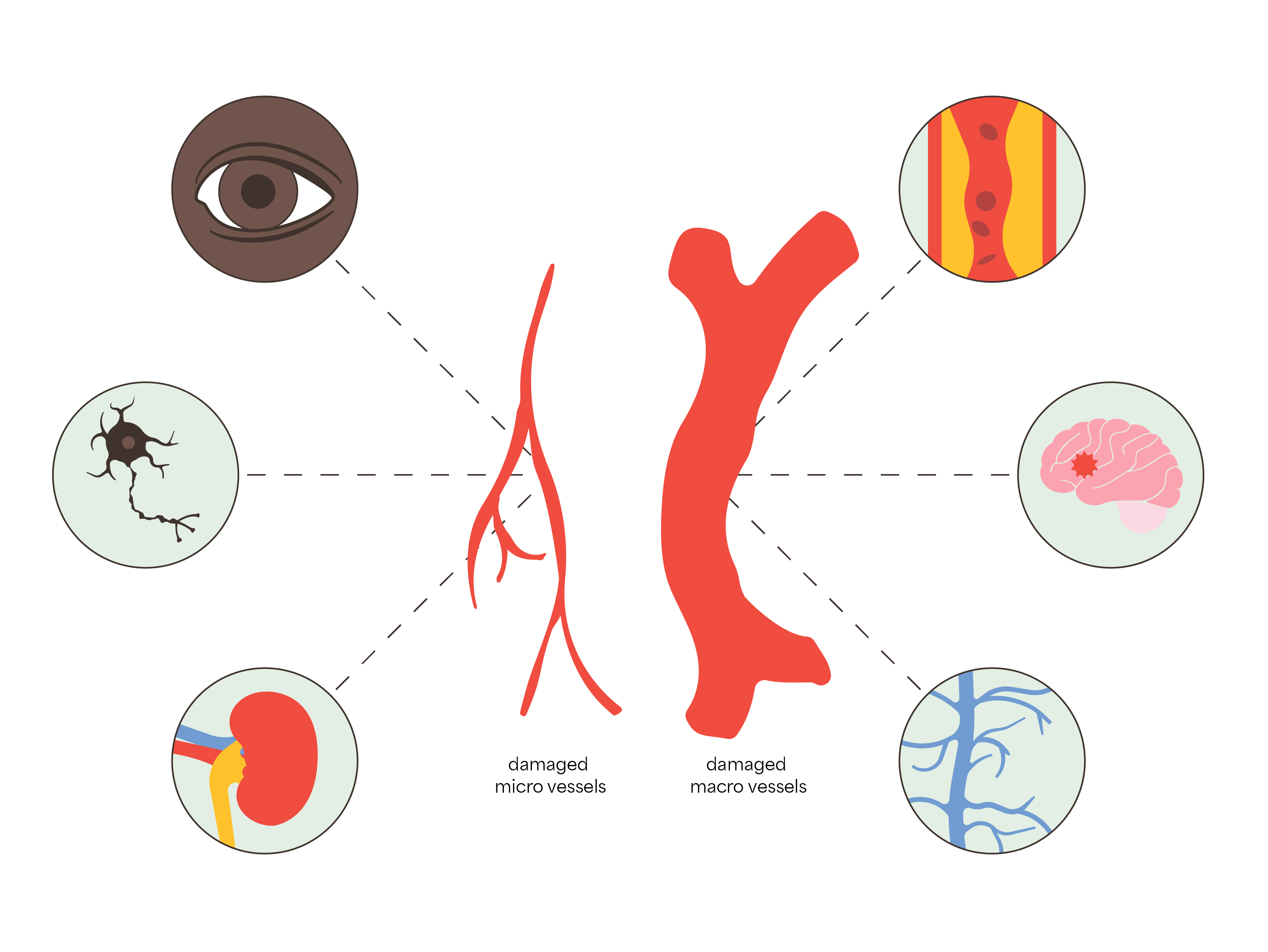
Damage to micro blood vessels can cause vision problems, nerve damage, and kidney disease.
Damage to macro blood vessels can lead to heart disease, stroke, and poor circulation.
Texas is experiencing a diabetes crisis.
Recent population health data collected by the state suggests that nearly half of all Texans are experiencing either type 2 diabetes or prediabetes.
Imagine a football stadium at full capacity, approximately 72,000 people
2.7 million Texans have been diagnosed with diabetes
That’s 37.5 stadiums full of people.
7.1 million Texans have prediabetes
Of the remaining 20.9 million Texans who have not been diagnosed with diabetes, approximately
621,000 have diabetes and do not know it
Clear disparities in diabetes prevalence
The 2024 edition of EHF’s annual health tracking survey revealed that almost half of Texas adults have diabetes experience in their household, meaning that they themselves (the survey respondents) or someone in their household has type 2 diabetes or prediabetes.
Of these households with diabetes experience (46%), EHF’s survey has surfaced several disparities:
Black and Hispanic households are more likely to experience diabetes
Household diabetes experience is more prevalent among suburban and lower education adults
EHF’s survey also indicates that households with diabetes, which make up nearly half of all Texas households, are more likely to have difficulty affording health care

Citing data from the American Cancer Society, the Texas Diabetes Council estimates that the mortality rate of diabetes-related complications is greater than many types of cancer.2
Texans' perspectives on diabetes prevention
In 2023, the Texas Diabetes Council released their annual State Plan to Prevent and Treat Diabetes and Obesity, outlining policy recommendations that would bring together diabetes stakeholders, such as the American Diabetes Association, the Association of Diabetes Care and Education Specialists, healthcare systems, health plans, etc. In addition to clinical recommendations, the TDC has recognized the importance of addressing disparities in non-medical drivers of health in the prevention and treatment of diabetes. Citing information from the American Diabetes Association’s Health Equity Bill of Rights, the TDC says social determinants of health can account for up to 60 percent of diabetes-related health outcomes.
Between October 18 and December 19, 2023, SSRS conducted EHF’s annual health tracking survey. With this year’s edition of the survey, we asked Texans to weigh in on possible strategies, taking place both in and outside the doctor’s office, to address prediabetes across Texas.
Hover over each strategy to reveal Texans’ perspectives:
preventative health care
66% of Texans say increasing access to preventative health care, including screenings for diabetes, would be very effective in diabetes prevention
reduced-cost health insurance
eating healthier and getting more exercise
76% of Texans with diabetes experience in their household say they should be eating healthier and 73% say they should be eating healthier
discussing diabetes risk
Six in ten Texans say encouraging doctors and nurses to discuss diabetes risk would be effective in diabetes prevention
educational resources
preventative health care, including screenings for diabetes
Q: What actions could officials take to prevent diabetes?
eating healthier and getting more exercise
encouraging doctors and nurses to discuss diabetes risk
Six in ten Texans
providing free or reduced-cost health insurance to low-income Texans
Q: What actions could officials take to prevent diabetes?



educational resources and community classes
About half of Texans also say providing educational resources and community classes on healthy eating would be effective
Moving Forward
For Texas to fully realize its great potential, all Texans must have the ability to thrive. Equity, specifically health equity is an essential part of that future. Elevating the voices of Texans through polling has the ability to influence health policy choices and provide Texans’ opinions about healthcare and health conditions. With that, each poll contributes to our central goal of improving health opportunities for all Texans.
Citations
American Diabetes Association. The Burden of Diabetes in Texas. Published March 2024.
Texas Diabetes Council. 2023 State Plan to Prevent and Treat Diabetes and Obesity. Published November 2023.